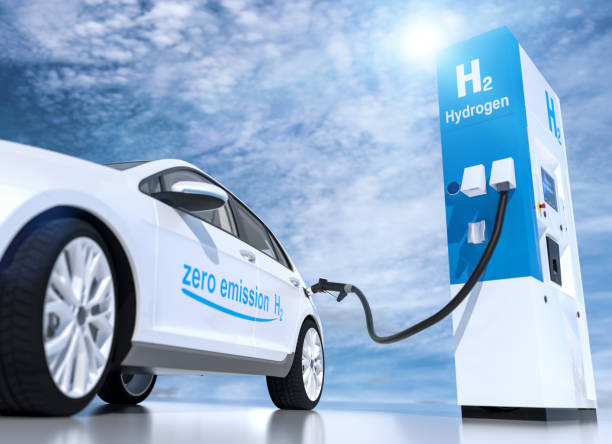
Under the Hood: The Intriguing Mechanics of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
Imagine a world where vehicles emit only water as a byproduct, where oil changes are a thing of the past, and where the term 'range anxiety' is banished from our motoring vocabulary. Welcome to the realm of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), a technology that promises to revolutionize our driving experience while making a significant contribution to a cleaner environment.

The Genesis of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
FCVs are not a new concept. The fundamental technology of converting hydrogen and oxygen into electricity dates back to the 19th century. However, it was only in the 1960s that General Motors first developed the Electrovan, the world’s first hydrogen fuel cell vehicle. Since then, significant advancements have been made, with automobile giants like Toyota and Hyundai now offering commercially available FCVs. But what exactly is a fuel cell, and how does it propel a vehicle?
The Heart of the Matter: Fuel Cells
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (oxygen) into electricity. In an FCV, this electricity powers the electric motor that drives the vehicle. The only byproduct? Water. This process is not only clean but also highly efficient, with fuel cells converting up to 60% of the energy in hydrogen into useful power, compared to a maximum of about 35% for internal combustion engines.
The Current State of Play: Industry Trends
Although still in its infancy, the FCV market shows promise. According to a report from Grand View Research, the global FCV market size was valued at USD 2.6 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.5% from 2021 to 2028. Governments worldwide are encouraging the development and adoption of FCVs through various incentives and regulatory measures, recognizing their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The Road Ahead: Impact, Benefits, and Challenges
The impact of FCVs could be profound. They offer a sustainable transportation solution that can significantly reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, FCVs have a longer driving range and faster refueling time compared to electric vehicles, addressing two significant pain points for electric vehicle adoption.
However, the path to widespread adoption is not without challenges. The availability of hydrogen refueling stations is limited, and the cost of producing, storing, and transporting hydrogen is high. Furthermore, the current process of producing hydrogen is largely dependent on natural gas, undermining the environmental benefits.
In conclusion, FCVs represent a promising facet of our automotive future. While there are hurdles to overcome, the potential benefits are significant. As the technology advances and becomes more accessible, we may soon see ourselves driving into a cleaner, greener future, powered by the most abundant element in the universe - hydrogen.